INDIA: Role of Geo Spatial Technology in Building Nation

India being a seventh-largest country (3.29 million sq km), fifth-largest economy (GDP $2.96 trillion) and second highest population (1.37 billion) in the world have various challenges in different sectors to sustain the growth and development of the nation. To bridge the social and economic disparity between different sections of society India needs a technological advancement and empowerment of citizens to enhance its system. In the 1980s, India adopted GIS technologies, India is using Remote Sensing Satellites, mapping, Geospatial database system, and other tools. In the early 2000s, a crucial step was taken which was considered to be impossible at that time as creating a blueprint for such a big project is next to impossible. India wants to create its own National Spatial Data Infrastructure. Indian democracy has 3 pillars and the fourth one is considered to be the information sector and this Geospatial database infrastructure is a crucial component of that pillar. The plan is to build a unified information infrastructure using GIS technology. The central government has added various reform projects, which provide tremendous opportunities to various sectors in India. The government does not want to limit it to the urban population but their plan was to provide e-services to each and every citizen which will ultimately lead to growth, prosperity, and sustainable development. Various sectors and industries are using Geospatial services in India for analysis of demography, disaster management, mapping, competitiveness, target-oriented marketing in agriculture, telecommunications, environmental management, wildlife management and conservation, oil and gas, public safety, infrastructure, logistics, etc. Development in India is not possible without the development of rural India which is a key part of Indian society, for their infrastructural development government has started several projects which include power, water supply, road construction, and natural resource management, and mandated the utilization of GIS technology in these projects. Projects like AgRIS, JNNURM, R-APDRP, etc are going well. India is investing huge amounts of money in spatial technologies, investment is increasing in different sectors as they know that today's investment will be fruitful and will definitely provide a blooming future.
Geospatial industry and technologies empowering Nation
The geospatial industry is providing services of management, integration, mapping, storage, display, and distribution of data which is linked with a particular location on earth. Products or tools have become an essential part of governance and resource management.
The geospatial industry is rapidly growing at the rate of around 12-15 percent annually, it will grow from $4 billion to $20 by 2025.
Visualization, measurement, and analysis of Earth's features, connected with instruments and equipment comprising geospatial technology.
The integration of private companies, NGOs, research institutes, academic organizations, and government agencies are part of the geospatial industry. They work together in different fields for the development and enforcement of technology.
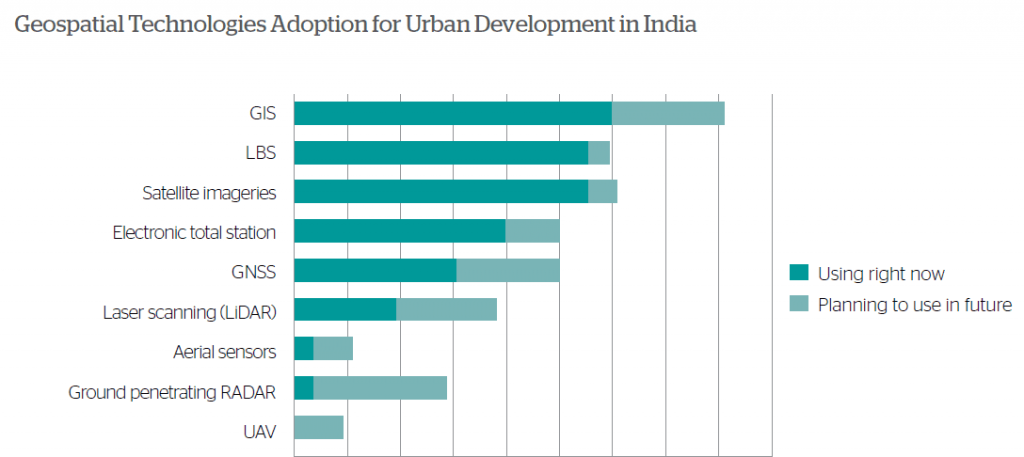
Global positioning system (GPS), Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) are famous and widely used technologies. Light detection and ranging (LIDAR) for remote sensing and Aerial photography, computer-aided design(CAD), location-based services(LBS) are used.
Spatial data infrastructure: it is designed to enhance the framework infrastructure of geographic data, metadata, users, and tools. These are interactively connected with each other to use spatial data. It is an efficient and flexible way. By this activity of human resources, policies, standards, and technology can be easily processed, maintained, used, and preserved adequately.
Software components comprise of the following units-
Software client: it can be browser or desktop GIS, used to analyze, display, and query spatial data.
Catalog Services: it used to discover, browse metadata, geospatial data, and spatial datasets.
Spatial data services: it includes delivering or transfer of data via using the internet network.
Processing services: data is processed (datum transformation).
Data repository: storing unit (spatial data, metadata)
GIS software: to work on spatial data, edit, add, analyze, etc.
India has created Indian National Spatial Data Infrastructure which aims to collaborate on different platforms by providing them resources at one platform.

GIS upgrading society by various tools and techniques-
1. Geospatial technology future of the city- ESRI India is working in the direction of planning smart cities in India by launching Geospatial tools that can be used to design 3D urban layouts for analysis and review, 3D models which look into the environment and other aspects. Creating 3D models using real-world 2D GIS data. It is really important to upgrade the city into a smart city, smart city into a green smart city, and so on, for that, we require smart planning, smart energy, smart infrastructure, public safety, smart waste disposal and management, smart services mechanism. Tools like GeoPlanner, CityEngine, and GeoEvent Processor are used by ESRI India.
GeoPlanner- used for infrastructure planning, designing, and plan in an online network with the integration of data and efficient spatial data analysis tools. It is a JavaScript-based web application which works in the direction of ArcGIS online and Geodesign- land-based planning activities. Users can analyze, create, and explore other alternatives planning scenarios for a better decision-making approach.
CityEngine is a software by which we can create a 3-dimensional design with proper visualization technology. Broadly used for improving urban development, architectural designs, etc. By collaborative effort, we can visualize, check feasibility, alter designs for better implementation. Main features are-
To transform 2D GIS data into smart 3D city models.
Flexibility and efficiency in building plans.
We can create a realistic context.
Collaborative and interactive approach while designing plans.
Singapore has developed 3D maps for developing smart cities, now India is also following the same path.
2.GeoEvent Processor: it is an ArcGIS server extension, it used to share real-time information with users and other systems. We can connect to real-time data streams by using a variety of sensors, which performs continuous processing and analyses data streams, and also sends relevant information and datasets to other users and systems. It is a new paradigm for Geofencing in India. GIS uses a server to detect, alert the user and authorities when some other device approaches or enters or leaves the geofenced territory.
3.Integrated coastal zone management project: It is a mega, five-year project to manage the coastline of India by Survey of India Hazard mapping survey is being done by using aerial photography and Satellite imagery techniques. There are 4 main components of this project
Activities are done to build capacity by mapping and demarcation of coastal hazard lines.
Areas that are considered to be environmentally sensitive are demarcated and mapping delineation is done.
Fragile areas along the coastline to be demarcated which includes mangroves, brackish water, wetlands, Coral reef, etc.
The project includes the building of a research center at the National Center for Sustainable Coastal Management, Anna University.
Conduct a training program for coastal zone management in India.
The project includes a coastline mapping of a 7,500-km area. The total cost of the project is around 125 crore.
Role in Indian economy
The geospatial industry has a positive impact on the country's total GDP growth and is growing rapidly at a faster rate. The projects which have been started so far, are those projects which require huge investment but these investments are generating revenue after a certain period of time. So for our developing economy, the Geospatial industry and tools both are beneficial and will surely help in the development of each and every section of society to reduce the social disparity in the society
Future Challenges
With the exponential growth in the geospatial industry, the demand is increasing and lack of manpower is a big issue. Skilled, technologically sound manpower is required in the industry.
The competition between the countries is increasing as market growth increases. Other Asian countries are big competitors.
More policies and planning required to accomplish future goals
The R & D sector requires more investment for the development of technological tools and advancement.
Data security is still the biggest challenge for any other country.
Conclusion: India is a developing nation and still building, we have opted for advanced technologies to build our nation. One being the Geographic information system, in every sector GIS and its tools are being utilized efficiently to enhance our system. We are using these tools day and night for our convenience and convenience is the indicator of development. Starting from mapping and today we have reached smart cities which includes security, delivery services, infrastructure, and many more. Besides this India has faced serious problems in rural areas, to overcome these problems geospatial information technology has been used to address them and to find the solution for the same. In Agricultural Management, soil management, water supply, road construction, environmental monitoring, natural resource assessment is being done using GIS and Remote sensing. These tools are efficient, economic, require less manpower, less time, and can be easy to access. We are using the GPS system on our phones. By using it we can travel anywhere, we have applications of Google maps which are nothing but geospatial data, so these applications have made our lives easier and more efficient in different manners. Still, there are a lot of challenges in this sector, which can be overcome by planning and integration of public and private sectors at all levels.




Comments
Post a Comment